The Meaning and Importance of the MARCH Acronym in Emergency Response

Emergency response in critical situations requires a systematic approach to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. One such approach that has gained significant recognition is the MARCH acronym, which stands for Massive hemorrhage, Airway, Respiratory, Circulation, and Hypothermia.
Let's delve deeper into the meaning and importance of each component in the MARCH algorithm.
Massive Hemorrhage
 |
Massive hemorrhage is often the primary concern in emergency situations, especially in combat scenarios where severe bleeding can lead to rapid deterioration. The prompt application of tourniquets, junctional tourniquets, and hemostatic dressings is crucial to control bleeding and prevent further complications. Studies have shown that hemorrhage is a leading cause of preventable death in combat, underscoring the critical importance of addressing massive hemorrhage effectively. |
Airway Control
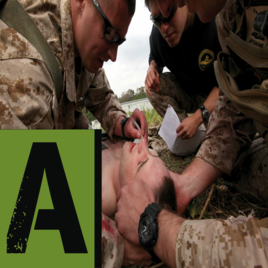 |
Ensuring a patent airway is essential for patients with traumatic injuries to facilitate adequate oxygenation and ventilation. Proper airway assessment and management, including interventions such as cricothyroidotomy when necessary, can significantly impact patient outcomes. Effective airway control is a key element in the MARCH algorithm and should not be overlooked in emergency response protocols. |
Respiratory Support
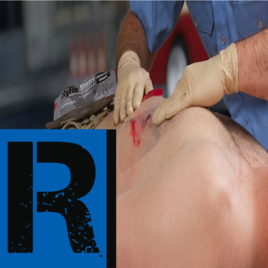 |
Respiratory support plays a vital role in managing trauma patients, particularly in identifying and addressing thoracic trauma and tension pneumothorax. Needle decompression may be required in cases of penetrating trauma to relieve pressure and improve respiratory function. Monitoring for respiratory distress and providing appropriate interventions are essential components of the MARCH algorithm. |
Circulation
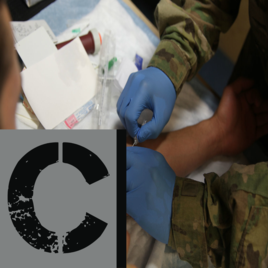 |
Optimizing circulation is critical in trauma resuscitation to prevent shock and maintain perfusion to vital organs. Assessing for signs of shock, evaluating blood pressure and pulse, and implementing fluid resuscitation strategies are key aspects of managing circulation in emergency situations. The MARCH algorithm emphasizes the importance of addressing circulation early to improve patient outcomes. |
Hypothermia
 |
Hypothermia can significantly impact patient outcomes in trauma care and is often a complicating factor in emergency response. Preventing and managing hypothermia through aggressive warming methods and maintaining body temperature are essential in the MARCH algorithm. Understanding the role of hypothermia in the trauma triad of death and addressing it effectively can improve patient survival rates. |
Head Injury
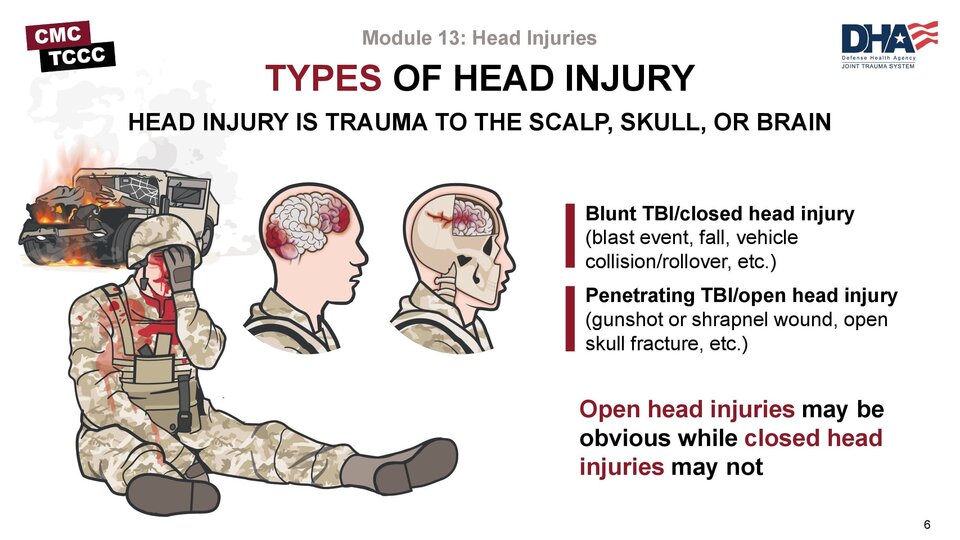
Head injuries require special attention in emergency response, as they can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if not managed appropriately. Monitoring for signs of cerebral herniation, implementing interventions to prevent secondary injuries, and addressing hypoglycemia when necessary are important considerations in the MARCH algorithm. Proper care for patients with head injuries can help mitigate the risk of long-term complications and improve overall outcomes.
By following the MARCH algorithm and understanding the significance of each component in emergency response, healthcare providers can deliver timely and effective care to patients in critical situations. The systematic approach offered by the MARCH acronym ensures that key priorities are addressed promptly, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and increased survival rates in emergency settings.

